2024 beckons with a promise of innovation — a year where AI and technology converge to redraw the maps of possibility.
Introduction
Welcome to a journey through the possibilities that 2024 holds for AI and technology. Here, each prediction is a potential window into a future filled with innovation, change and more importantly opportunity similar to the industrial revolution of the 1950’s. The 50’s witnessed the rise of digital computing, reshaping industries and societal norms. Today, artificial intelligence plays a similar role, forging the next industrial revolution.
Much like the the post-war technological boom, we are navigating 2024 with industries transforming, new skills in demand, and significant ethical considerations being raised. The views expressed here are all my own, and based on my personal, commercial, and academic experiences combined.
Table Of Contents — All Predictions & Trends:
1) Generative AI Leaps From Hype To Center Stage
Poised to redefine tech’s ecosystem, generative AI shifts from a hype-cycle balloon that’s “going to burst” to a core strategy and more of a sure thing, just as the airships are making a comeback.
For large enterprises it’s a paradigm shift in how they approach problem-solving and innovation, as they move from experimenting to adopting with generative AI. This technological course correction is akin to the transformative wave brought about by the early adoption of cloud technologies, suggesting a similar, if not greater, impact on the tech ecosystem.
The landscape of 2024, therefore, promises to be one where generative AI is not just a buzzword but a critical driver of technological advancement and business transformation. Where AI strategy is strategy.

2) The Next Generation Of Neural Networks Starts Emerging
With doubts forming on the general cognitive abilities of transformer architectures powering LLMs and the race for AGI has fuelled the research community searching for the next best thing. We have seen some recent advancements as well as developments in existing technologies:
These new model architectures are painting a future where AI’s capabilities could rival human cognition and the limitations of generative AI today. Research is early however expect to see someone take a leap of faith and break ground in this space.

3) Every Data Platform Launches Their Vector Data Solution
With the reliance on vector databases for generative AI, we will see all the key data platform players to bring to market their flavour for solving this solution. Although vector databases are not a new concept, they are not traditionally part of the “modern data stack” and have been in the past used for search engines and other types of machine learning.
Vector databases are a key requirement for more complex use cases of generative AI such as conversational memory, searching your documents (RAG), and also multi-modal solutions such as indexing images. It’s no surprise in mid-2023 we saw an explosion in demand following multi-modal models becoming more accessible.
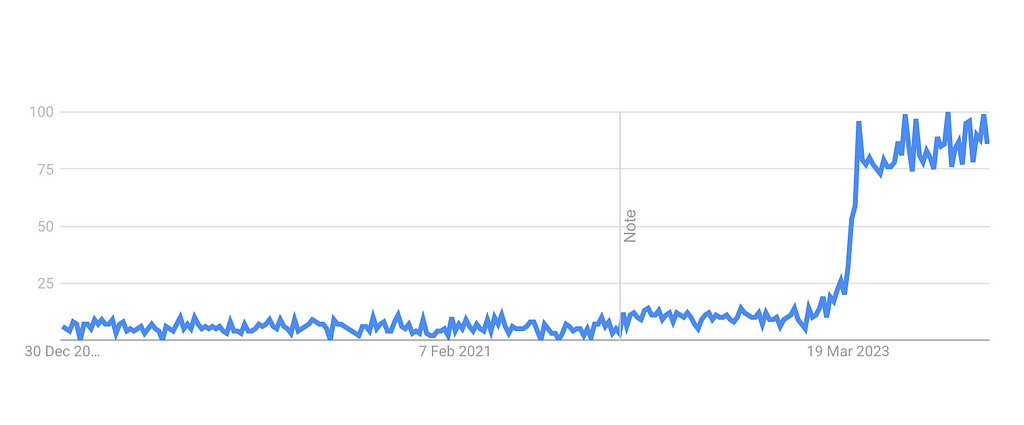
Demand for Vector Databases following OpenAI GPT-4 release in March 2023 — Google Trends (Worldwide)
With Databricks recently releasing their vector data solution we are likely to expect key modern data platform players such as Snowflake to follow this trend in 2024. Possibly other adjacent technology providers are also going to jump on the trend by providing various features and services. Nearly all database technologies will start calling themselves “vector stores” in 2024.
Alongside this adoption shift, we are likely to see skills expectation with senior data and software engineers to get more comfortable with concepts around vector indexes, semantic search solutions, embeddings and possibly even algorithms such as BM25.
To stretch we might see the acquisition or further funding rounds for some of the initial modern vector search solutions adopted by the Generative AI community such as Chroma, Weaveate, Pinecone, and Qdrant.
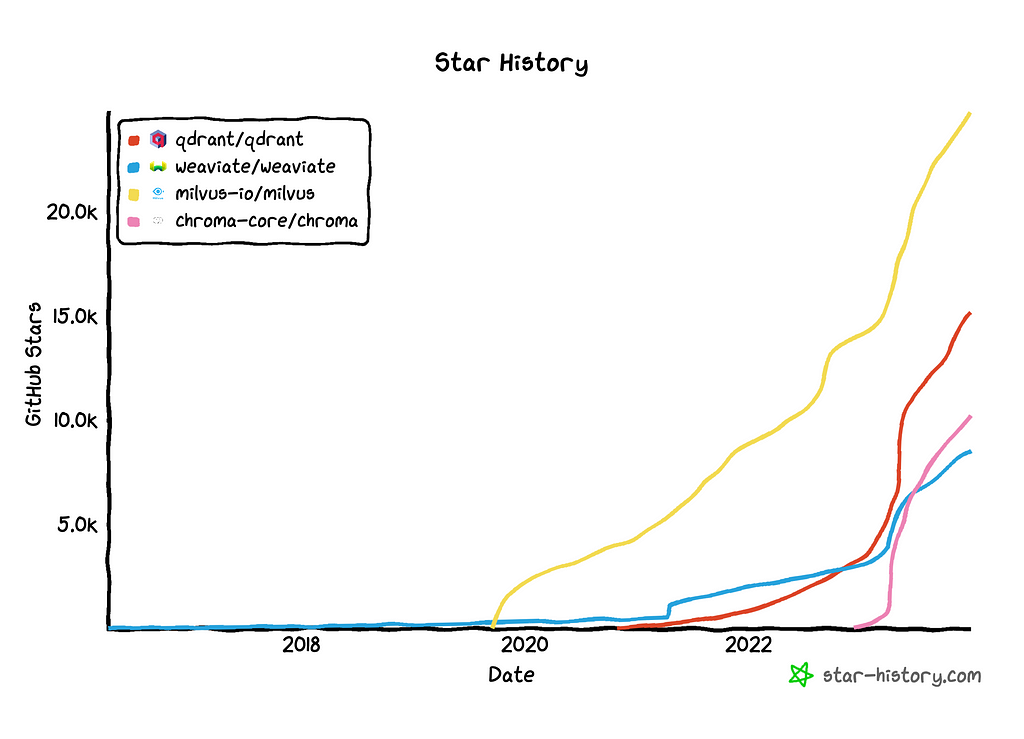
Github “stars” for open source vector database repositories. Growth aligns with GPT3.5 release — Source: Star-History & Github
In the open-source world of vector stores Milvus is currently the crowd favourite and established itself as the enterprise choice with its managed services, but recently Qdrant has made some exceptional headway with near exponential growth in 2023.
If you have some spare time read the four part detailed vector database breakdown given by fellow AI engineer Prashanth Rao for a great in-depth understanding of the capabilities and various providers of vector database solutions.
4) Rush To Control The Hardware And Platform Supply Chain
With the dominance of artificial intelligence there is an increasing importance to better control the supply chain end-to-end to hold the keys to innovation.
NVIDIA, for instance, a leader in chip manufacturing which has been a clear winner in the AI race. The question on everyone’s mind is whether NVIDIA will expand its horizons into the cloud computing realm, leveraging its hardware expertise to offer integrated AI cloud services. NVIDIA already has a cloud streaming service called Geforce Now offering high end graphics processing on-demand. Such a move could redefine the competitive landscape, offering NVIDIA a more direct influence over AI’s developmental trajectory.

Nvidia Share Price, Last 5 Years (NASD:NVDA) — Source: Nvidia Investor Relations
On the other side of the spectrum are cloud AI providers like Amazon and emerging AI players like Anthropic and Mistral. Their current reliance on external hardware sources for AI operations raises a crucial question: Will they follow in the footsteps of OpenAI, which has begun sourcing its own chips and Google with TPU’s and Coral AI? This strategy could signify a shift towards self-reliance and customization in AI hardware, potentially leading to more tailored and efficient AI solutions for the top AI providers.
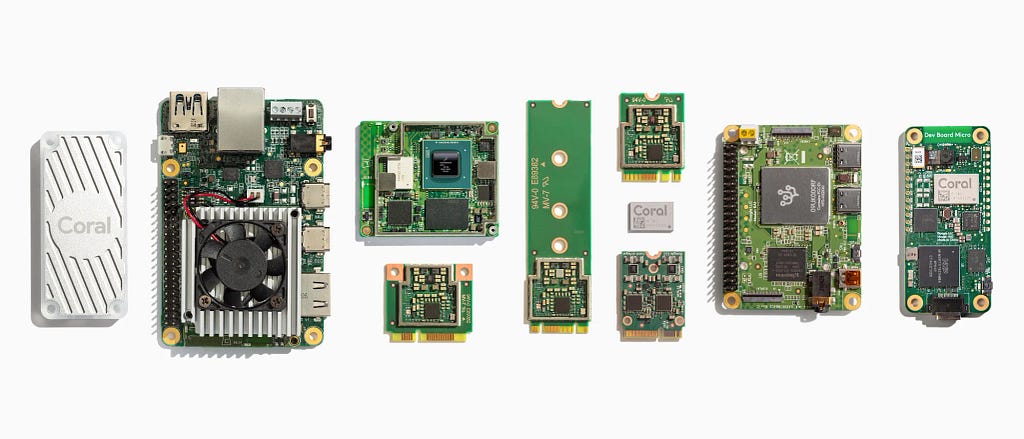

Google Coral — Local AI Development Boards and Hardware — Credit: Coral AI
As everyone in the underlying hardware layer of AI will be rushing to further control their supply chain. Will chip manufacturer NVIDIA move to cloud? Will cloud AI providers such as Amazon or the likes of Antrophic follow OpenAI in sourcing their own chips? Will mobile chip makers like Qualcomm be the winners as they power the new AI mobile devices and wearables?
The trend towards vertical integration of AI underscores a larger narrative: control over AI hardware is becoming synonymous with control over the future of tech. We will expect to see new players muscle into the purpose built AI chips to serve cloud players, countries rushing to fuel microprocessor development and finally OpenAI getting into the chip game in early 2024.
5) 2024 Is The Year Of The AI Wearables & XR
This year, we’re witnessing an intimate revolution in how we interact with technology, with the world of AI and wearables fusing alongside extended reality (XR) devices. These devices are not just gadgets; they’re extensions of our digital selves, blending seamlessly into our daily lives.
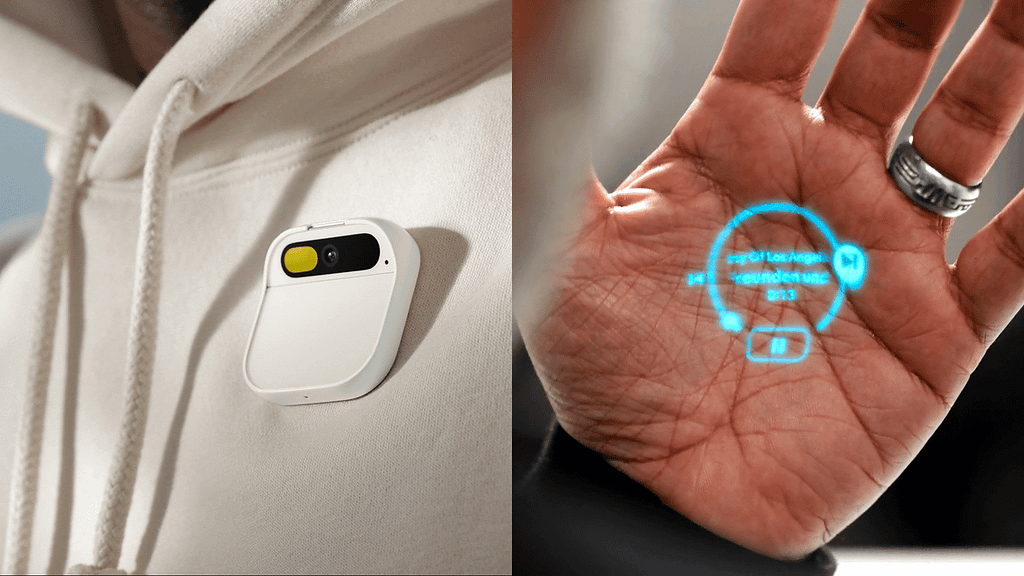
Humane AI Pin — Source: Humane
Humane AI’s Pin (powered by Qualcomm Snapdragon processors) and Tab are redefining the wearable landscape. These devices offer a glimpse into a future where wearables are no longer just about tracking health metrics or receiving notifications. They are about enhancing human interactions, offering real-time AI assistance, and providing an augmented experience of the world around us.

Rewind AI Pendant — Source: Rewind
Rewind, another breakthrough product, is revolutionizing how we capture and relive our memories. Imagine a device that not only records moments as we experience them but also allows us to revisit, understand, reflect on our memories.
But it’s not just the new players making waves. Tech giants like Apple and OpenAI are stepping into the wearable arena, promising to bring their colossal innovation capabilities. Apple, with its track record in creating trendsetting devices, is highly likely to introduce wearables that integrate seamlessly with its ecosystem within or alongside their XR Apple Vision Pro, offering unparalleled user experiences.
OpenAI, on the other hand, could leverage its expertise in AI to introduce wearables that bring advanced AI functionalities right to our fingertips (or wrists). The potential for AI wearables that interact with generative AI models like ChatGPT is particularly exciting, offering a blend of convenience and intelligence unlike anything we’ve seen before.
Meta is another key player to watch. Their foray into VR wearables has already shown us the potential for immersive digital experiences. As they continue to innovate in this space, we can expect wearables that not only augment reality but create entirely new realms for us to explore and interact with.
In 2024, AI wearables are set to move beyond mere technology. They are becoming personal companions, digital assistants, and gateways to new realities. They represent a shift towards a more intimate and interactive relationship with technology, one where our digital and physical worlds intertwine seamlessly. This year, we’re not just wearing technology; we’re living it.
6) AI Agents Will Start Communicating With Other AI Agents
Envision an ecosystem where specialized agents, each with its unique expertise and knowledge base, interact and collaborate. With the development of AI “agents” we will continue to see the growth in this space heading into 2024.
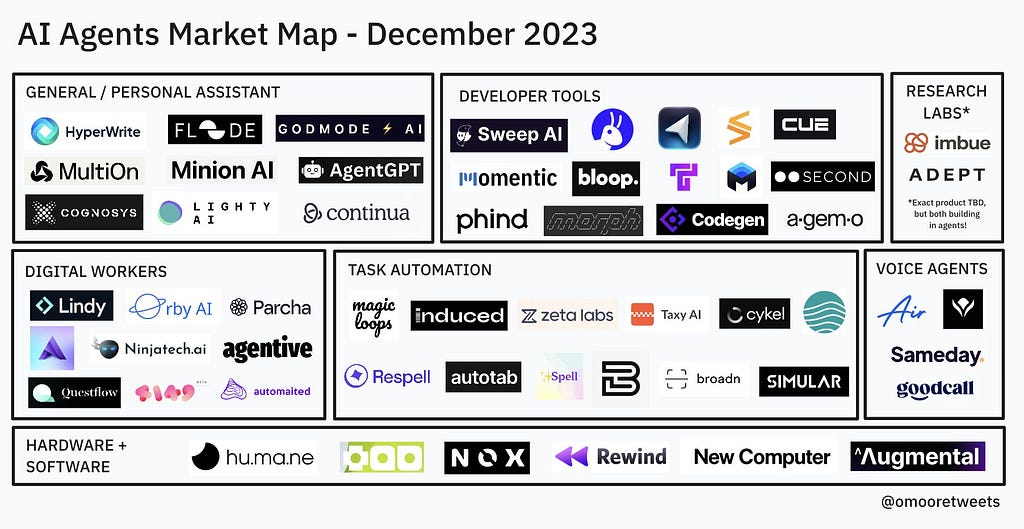
AI Agents Market Map Dec 23 — Credit: Olivia Moore
We will see the advent of agents going beyond supporting individual needs like writing my email, solving a customer support issue or ordering my groceries to an ecosystem where agents will start to interact with other agents. This paradigm shift revolves closely with the concept of data products, where enterprises will have the opportunity to monetize their agents in the same way they did with their models and datasets. This will foster a new ecosystem of interconnected, intelligent agents.
We are seeing robotics and humanoids from companies such as Boston Dynamics and Tesla having to look at solving this problem as various robots need to co-exist and locally communicate the decide how to carry out a task.
Companies with strongholds of data within given verticals like Bloomberg (finance) and LexusNexus (law) are poised to be potential frontrunners in this domain. Bloomberg, with its stronghold in finance data, could introduce sophisticated finance agents and have already started on their own LLMs, while LexusNexus could leverage its vast legal information repository to develop legal agents. These agents, powered by their respective deep moats of data, would not only serve their direct users but also act as invaluable resources for other enterprises and systems to power a new digital workforce.
Expect to start seeing new agent solutions beyond digital workforce to agent orchestration, management, monitoring as well as players in the digital robotic process automation space such as UiPath as well as humanoid advancements for manufacturing and plant work start to play into this space with their existing experience of automating and robotics systems at scale.
7) Generative AI Modalities Will Expand
Going beyond the text, code, image, video and audio to new more immersive modalities and senses such as 3D, genomics, smell, taste and will start to come into the market in early forms.
Generative spatial AI to generate new town layouts — https://www.generativespatialai.com/
Generative AI is set to grow out of its current boundaries of text, code, image, video, and audio. We will embrace more immersive modalities that help science with protein structures and materials or engage additional senses like 3D, smell, and taste. These novel modalities are expected to emerge in their early forms, signaling the next wave of Generative AI use cases.
The rise of autonomous AI agents and multi-modal models, coupled with advancements in wearables and extended reality (XR), is paving the way for a more immersive and interactive experiences for consumers.
With recent 3D modelling technologies (Gaussian splatting) were videos can be converted into 3d virtual realities we will see this grow to new heights with generative technologies.

A-Lab Berkeley, Robot Testing New Materials — Credit: Marilyn Sargent/Berkeley Lab
The biggest impact will come from material sciences and genomics. GNoME model developed by Google Deepmind has been used already to make breakthroughs in material sciences, discovering new crystal structures driving better batteries to more efficient computers.
These fields such as sciences are where the most profound research advancements are likely to occur.
8) Consumers & Regulators Push For More Democratized AI
The will be a continued push towards greater accessibility and inclusivity with AI, but challenges remain due to the complexities and costs of developing foundational AI models. This dichotomy sets the stage for increasing public demands for transparency and ethical oversight in AI.
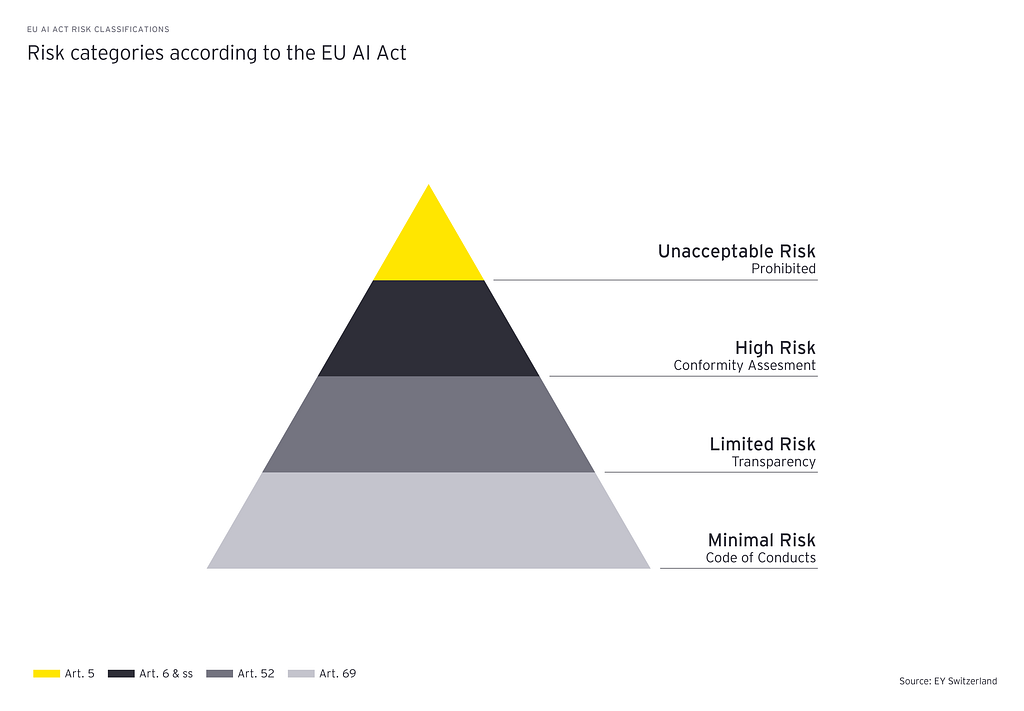
EU AI Act — Proposed Levels of Risk — Source: EY
Concerns over privacy and the societal impact of AI are driving consumers and regulatory bodies, especially in regions like the EU where GDPR was the catalyst to modern data privacy laws, to advocate for more stringent governance of AI. This year, we expect to see strides in establishing frameworks for auditing AI models, standardizing accuracy, and introducing “report cards” for AI systems but there is still a long way to go.
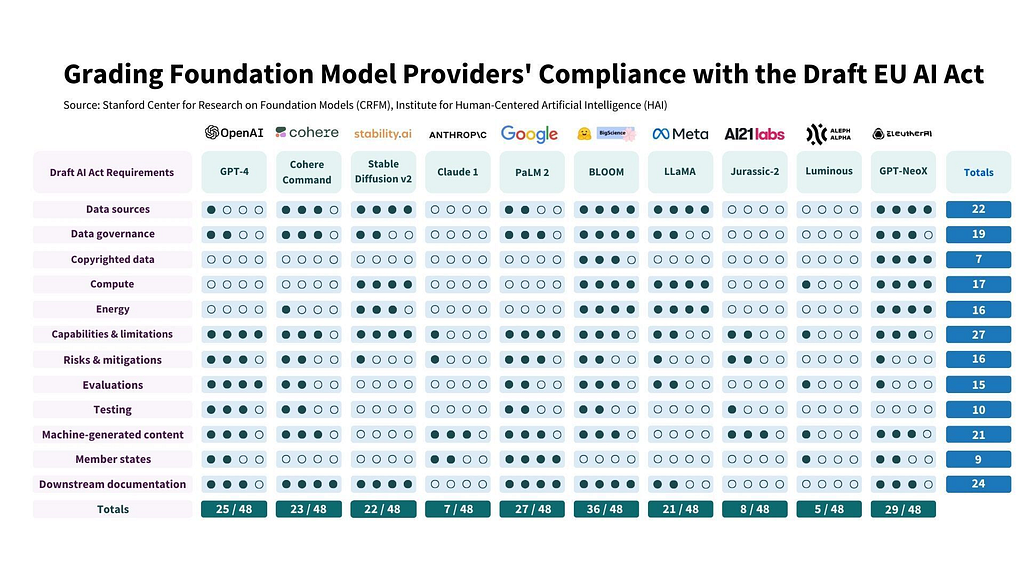
Do Foundation Model Providers Comply with the Draft EU AI Act? — Source: Stanford CRFN
The focus on risk management in AI will become more pronounced. Enterprises will navigate a landscape where AI is not only a tool for innovation but also under close regulatory scrutiny. Unified frameworks and standards will emerge, guiding businesses in responsible AI adoption and ensuring that AI’s integration into mainstream society is safe and aligned with public welfare.

9) The New Era of AI-Infused Marketing Strategies
The marketing domain, traditionally commanding a lion’s share of enterprise budgets, is now navigating through a transformative landscape. The catalyst? The rise of chat-based tools like ChatGPT. These innovations are potentially leading to a noticeable decline in traditional search volume, fundamentally altering how consumers engage with information.
Greg Sterling ?? on Twitter: "A report from BofA argues that Google's search market share is down ever so slightly and attributes that to ChatGPT. (I question that.) I think a more interesting metric to look at would be search frequency; are people conducting as many searches on Google as they used to? pic.twitter.com/S9iBXR4biP / Twitter"
A report from BofA argues that Google's search market share is down ever so slightly and attributes that to ChatGPT. (I question that.) I think a more interesting metric to look at would be search frequency; are people conducting as many searches on Google as they used to? pic.twitter.com/S9iBXR4biP
In this evolving scenario, marketers find themselves at a crossroads. The ability to influence or monitor brand mentions in these AI-driven dialogues is still in its nascent stages. Consequently, there’s a growing trend towards adapting marketing strategies for a generative AI world. This adaptation involves a strategic reliance on traditional media in the short term, leveraging its reach and impact to build and sustain brand presence.
Simultaneously, we are witnessing a significant shift in the technological landscape. The move from browser-based tools to on-device applications is gaining momentum. Leading this charge are innovations like Microsoft Co-Pilot, Google Bard on devices such as Android, and the anticipated launch of Apple’s own large language model (LLM) sometime in 2024. This transition indicates a paradigm shift from web-centric interactions to a more integrated, device-based AI experience.

New Microsoft Surface X expected late 2024 — Source: Microsoft
This shift extends beyond mere convenience; it represents a fundamental change in user interaction paradigms. As AI becomes more seamlessly integrated into devices, the distinction between online and offline interactions becomes increasingly blurred. Users are likely to interact with AI in more personal, context-aware environments, leading to a more organic and engaging user experience. For tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Apple, already entrenched in the marketing services world, this represents an opportunity to redefine their offerings.
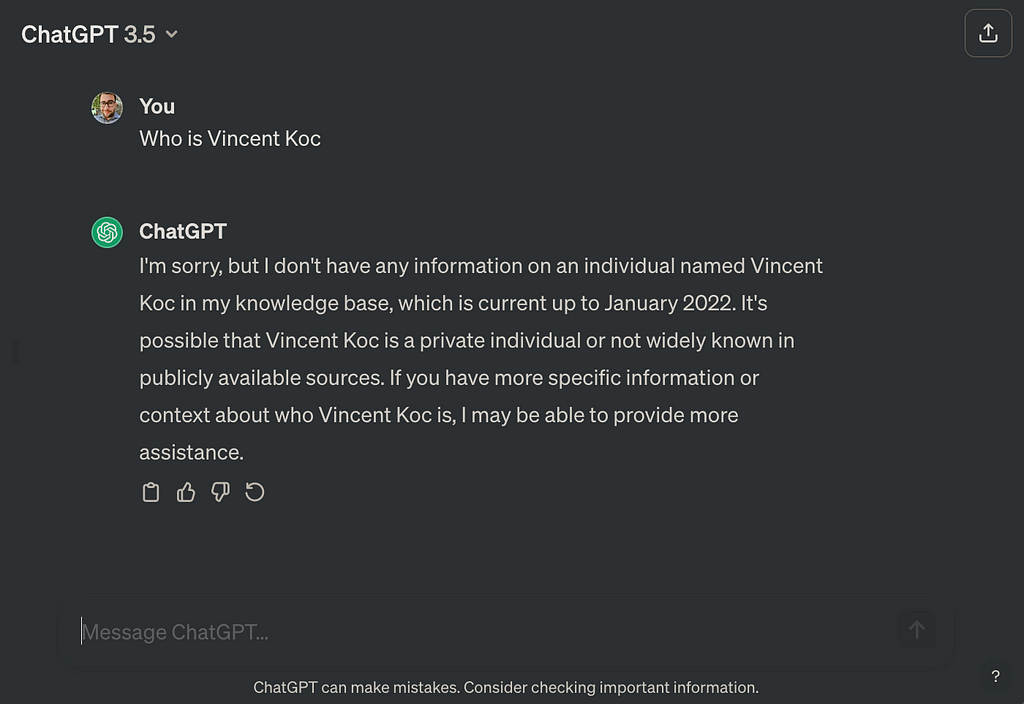
ChatGPT not knowing who I am — Source: Vincent Koc and OpenAI ChatGPT
We can anticipate the emergence of new “answer analytics” platforms and operating models in marketing to support answer engine optimisation. These tools will likely focus on understanding and leveraging the nuances of AI-driven interactions but potentially better leverage the training data to understand how the results might be portrayed for a given brand or product.
Digital marketeers will start to think more deeply about how they are indexed in these training datasets same as they once did with search engines.

Screenshot of Top Domains Crawled by Commoncrawl, Dataset used to train most Large Language Models — https://commoncrawl.github.io/cc-crawl-statistics/plots/domains.html
Moreover, the potential launch of ad-sponsored results or media measurement tools by platforms like OpenAI could introduce a new dimension in digital advertising. This development would not only offer new avenues for brand promotion but also challenge existing digital marketing strategies, prompting a reevaluation of metrics and ROI assessment methodologies.
As LLM’s migrate into devices, moving away from traditional web interfaces, the marketing landscape is poised for significant changes. Marketers must adapt to these shifts, leveraging both traditional media and emerging AI technologies, to effectively engage with their audiences in this new digital era. This dual approach, combining the impact of traditional media with the precision of AI-driven analytics, could very well be the key to success in the rapidly evolving marketing landscape of 2024.

10) The “Garbage In, Garbage Out” Dilemma Intensifies
As organizations increasingly pivot towards leveraging generative AI models and developing their own fine-tuned solutions, the spotlight falls sharply on the quality of input data. The classic saying in data management circles of “garbage in, garbage out” is bubbled up again as data quality is now back on the table.
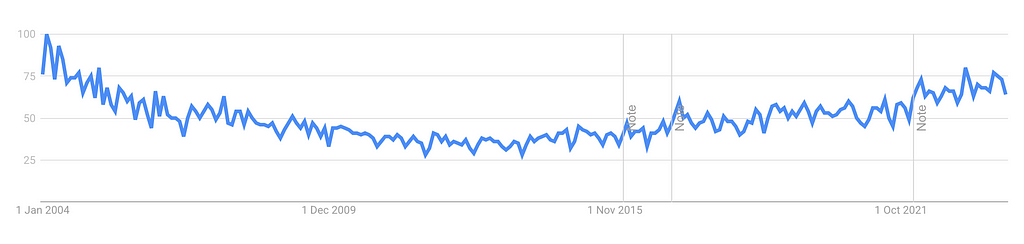
Trend for: Data Quality Topic — Source: Google Trends Worldwide
Organisations and leaders confront the harsh reality that high-quality, accurately labeled data is the cornerstone of effective AI deployment. The issue goes beyond the obvious availability of data; it’s about its relevance, accuracy, and the context it provides. Issues of bias and misguided training data can spell disaster for the output of a model.
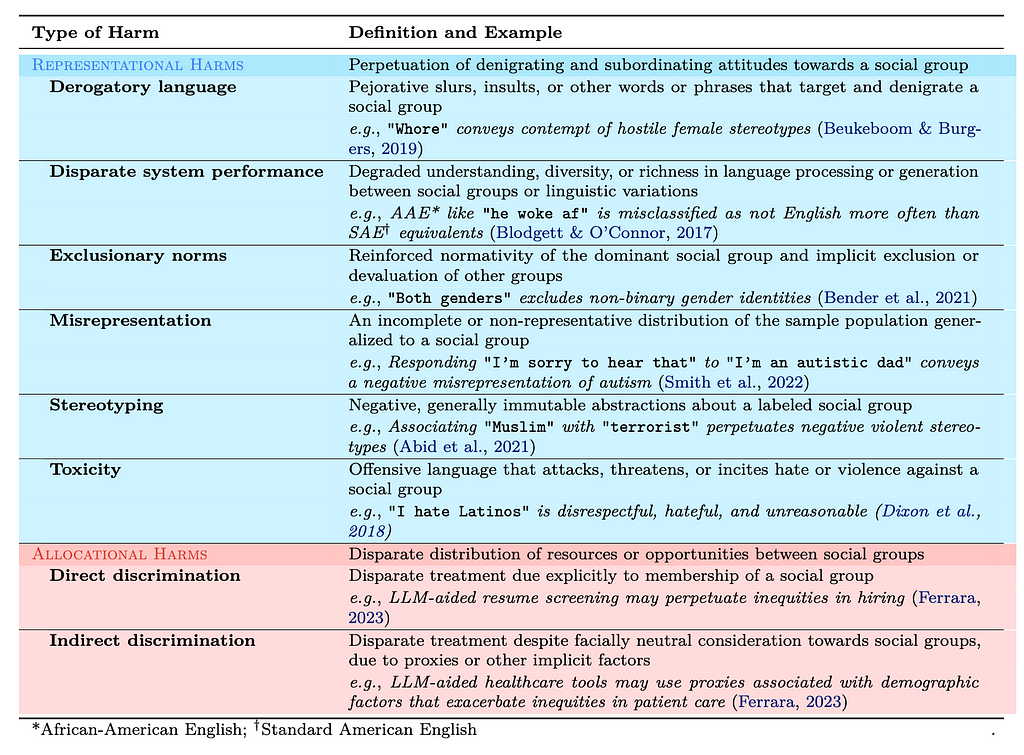
Range of biases have been found in a range of training data used by Large Language Models. — Source: Bias and Fairness in Large Language Models: A Survey — arxiv
However, the challenges don’t stop there. Existing data and AI pipeline technologies, which once seemed adequate, are now being pushed to their limits. They are often found wanting in the face of the nuanced demands of advanced AI models. This gap between capability and requirement necessitates an evolution in data processing tools and methodologies.
Furthermore, the pursuit of AI excellence comes with its own set of logistical hurdles. The intensive compute power required for these sophisticated AI models translates to a substantial demand for GPUs.

Meme depicting the “GPU shortage”
But this isn’t just about having the financial muscle to invest in hardware; it’s about the availability of these resources in the market. As more players enter the AI arena, the scramble for GPUs intensifies, leading to potential bottlenecks in AI development and deployment which adds further complexity to the ability for organisations to adapt to the normal in AI.
As 2024 unfolds, we witness a renewed focus on data quality and infrastructure enhancement, shaping the trajectory of AI development.

11) Purpose Built Smaller Foundational Models Commonplace
2024 might very well be the year of the small foundational models. These specialized, purpose-built AI models are set to take center stage, outshining their generalized counterparts in efficiency and precision.
Organisations now have a number of options of using readily trained generalised large language models such as OpenAI GPT, Google Bard, Anthropic Claude [RL model in chart below] or venture into the world of building your own.

LLM development stages, pioneered by the InstructGPT paper, leading to ChatGPT. This figure is adapted from Chip Huyen’s post “RLHF: Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback” — Source: Argilla
With options to fine-tune which is taking the base/foundational language model but teaching it new things (as you would imagine fine tuning a car to go faster) or go deep into creating your own foundational (base) models altogether.

Open AI GPT Custom Model for Enterprise — Source: OpenAI
With generalised models such as the GPT models with 100 billion parameters (or “switches” in its model programming) would cost roughly upwards of $4million to rebuild. OpenAI has also recently started offering a service for enterprise to “build your own GPT” for pricing starting from $2–3million.
Organizations that have either developed their own foundational models or fine-tuned existing ones to their specific use-cases are poised for success. This approach aligns with the 80:20 rule, where the focus is on smaller, tailored models that cater to specific needs rather than attempting to appeal to the masses with generalized solutions.
The true value for organizations lies in the ability to develop these purpose-built models for discrete tasks. Not only do these models offer higher accuracy and relevance, but they also present new monetization opportunities. In a world increasingly driven by specialized needs, these models become invaluable assets, offering solutions that are both effective and economically viable.
Moreover, the trend is shifting away from relying solely on large, general-purpose models as they are not quite perfect for every need. Many organizations have built solutions on top of these broad models, acting as “thin wrappers” that offer limited scope for customization and scalability. While these solutions may have been a stepping stone, they are unlikely to provide the long-term value that developing proprietary models can offer.
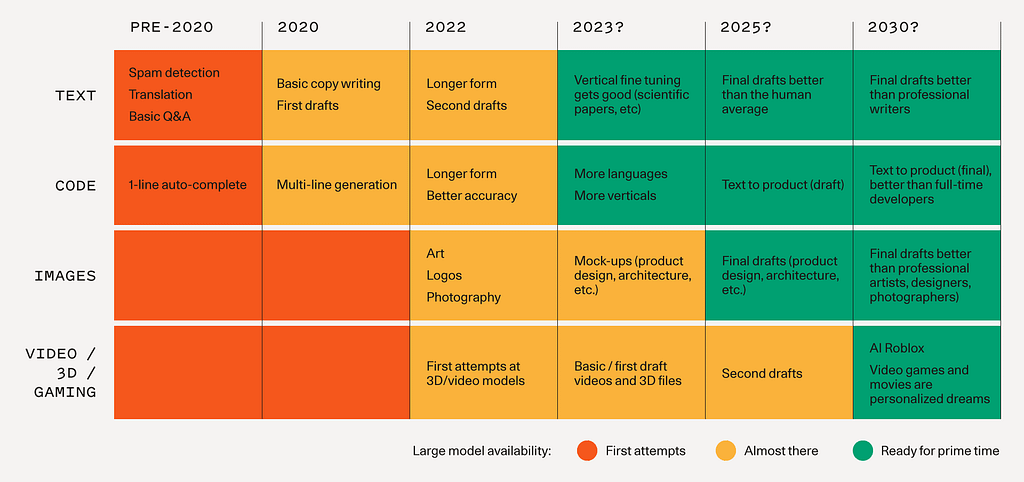
Generalised Model Availability and Quality Prediction — Source: Sequioa Capital
The winners in this evolving landscape will be those who invest in developing their own models generalised or small foundational models to plug gaps in the generalised space. This strategy not only increases accuracy and effectiveness but also reduces cost overheads. Smaller models are not only cheaper to run but also quicker to adapt and easier to manage.
As we look towards 2024, it’s clear that the ability to create and leverage small foundational models will be a key differentiator in the competitive AI market. This shift marks a significant move towards more personalized, efficient, and economically sound AI solutions.
12) The Dawn Of AI Marketplaces For Agents
AI marketplaces are emerging as adaptive and responsive platforms, reshaping the way we think about technology transactions and interactions.
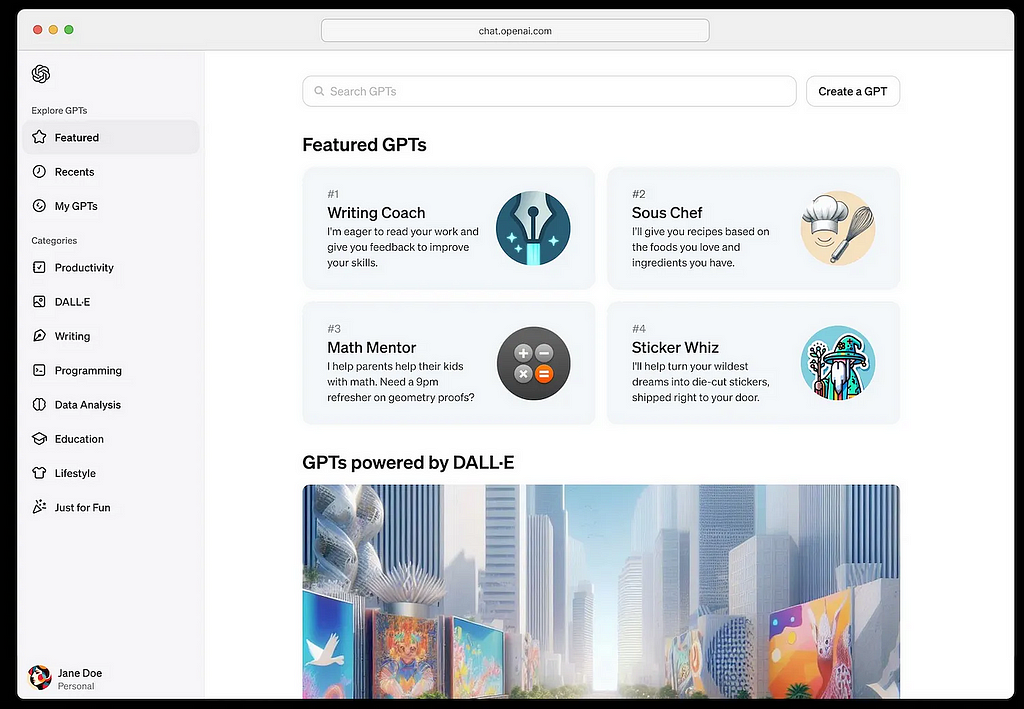
OpenAI GPT Store, Launching in 2024 — Source: OpenAI
Leading the charge, OpenAI is poised to unveil its much-anticipated “GPT marketplace” in early 2024, setting a new benchmark in the AI arena. This move is expected to open the floodgates, with other tech giants like Meta quickly following suit. We could witness an array of players, from established giants like Amazon, Apple and even Bytedance to emerging startups, diving into this space.
But the ripple effect of this revolution extends beyond traditional tech entities. With the growth of autonomous agents and the surge in wearable technology, there will be the Apple iPhone and App Store moment again. Developers will see this as the next gold rush of opportunity.
In this transformative phase, the AI marketplace phenomenon is expanding its reach from B2B to B2C sectors. We’re likely to see a diverse range of players trying their hand at this, each bringing unique value propositions to the table. From consumer-focused AI applications to enterprise-level solutions, the spectrum of offerings in these marketplaces will cater to a wide array of needs and aspirations.
13) AI Products Will Go Beyond SaaS Model
With the proliferation of AI marketplaces and tools, traditional pricing strategies are being re-evaluated, making way for innovative approaches that cater to the unique nature of AI services.
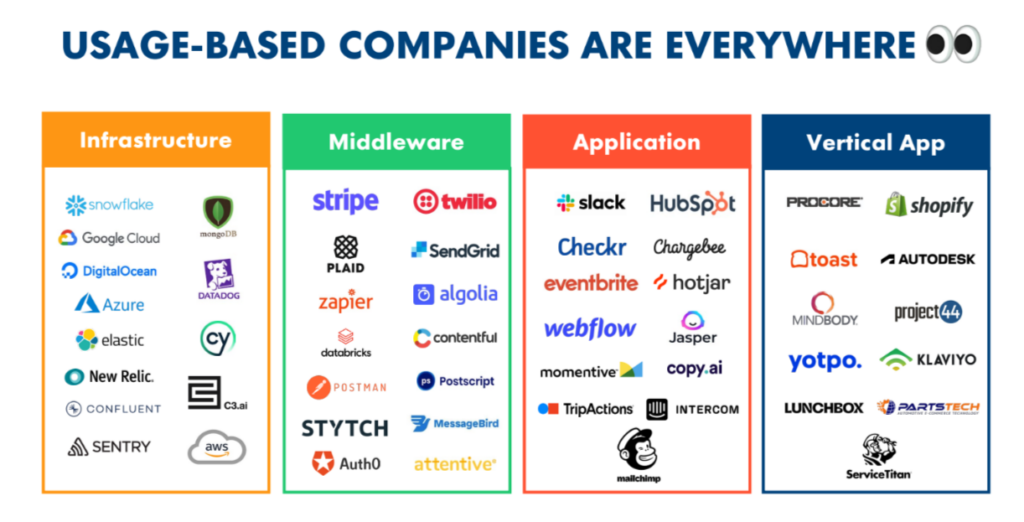
Usage Based Companies — Source: Open Venture Partners
We are likely to witness a significant shift from the conventional app store pricing model to more dynamic, consumption based billing systems. These models, reminiscent of utility billing like phone lines, are poised to become more prevalent, aligning with the concept of renting AI agents. In this setup, customers would pay based on the extent and nature of their AI usage, offering a flexible and potentially more equitable pricing structure.
But the evolution doesn’t stop there. The increasing adoption of AI marketplaces and tools is also paving the way for varied pricing strategies and novel business models. This change is driven by the need to accommodate a wide range of AI applications and services, each with its own value proposition and usage patterns. This could see the trial of both the revenue share (App Store) or the royalties on usage (Spotify) model for developers and their AI services or agents on marketplaces.
Another emerging model could be performance-based pricing, where charges are aligned with the outcomes or results delivered by the AI tool. Such a model would be particularly appealing in sectors where AI’s impact can be quantitatively measured, like in marketing analytics, financial forecasting, or even creative industries.

Bundled vs Unbundled Strategies in Pricing — Source: Matt Brown
Furthermore, as AI continues to penetrate various sectors, cross-industry partnerships could give rise to bundled services. These bundles could combine AI tools with traditional software services, offering a comprehensive package that addresses a wider array of business needs.
The onset of these new pricing models and strategies reflects a marketplace that is rapidly adapting to the unique challenges and opportunities presented by AI. As businesses and consumers alike become more familiar with AI capabilities, the demand for flexible, transparent, and value-aligned pricing models will likely intensify.
14) BYO AI Movement Pushes Need For Secure Digital Identities
Expanding modern and generative AI tools will lead the expansion of digital footprints necessitating secure, portable digital identities, where the challenge is to balance robust security with user accessibility. Users will expect a personalised experience where preferences, history and context will be key to using many AI services across the web.
Banks and e-government platforms are emerging as potential custodians of these single digital identities and personal preferences. This consolidation points towards a streamlined, more secure digital existence. But it’s not just about security; it’s about the seamless integration of our digital selves across various platforms.
“Bring Your Own AI” (BYO AI) ties directly into this. Imagine carrying your digital preferences, learning styles, and even shopping habits seamlessly from one digital interaction to another. This portability isn’t just convenient; it’s transformative. It allows for a level of personalization and efficiency previously unattainable. Wearable are also becoming integral to managing our digital identities. By constantly learning from our interactions, they evolve into personal data hubs that not only understand our preferences but anticipate our needs.
The integration of AI into work environments means that our digital preferences could automatically adjust settings in office applications, communication tools, and even physical workspaces. Imagine entering a meeting room where the lighting, temperature, and even digital displays are automatically tailored to your preferences.
However, this level of personalization and data integration raises questions about privacy and data usage. As these digital identities become more intricate and intertwined with AI, the potential for them to be leveraged for advertising digital experience providers for hyper-personalization is significant. This could lead to a new era of contextual advertising and consumer engagement, where promotions are not just targeted but deeply integrated into our digital personas.
This integration of identity with AI will redefine how we interact with technology, both in personal and professional spheres, leading to a more personalized, efficient, and connected existence. As we embrace this future, the importance of ethical considerations and privacy safeguards becomes more crucial than ever.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
As we look towards 2024, the potential of AI and technology to reshape our world is undeniable. Each of these predictions offers a glimpse into a future where innovation, responsibility, and inclusivity go hand in hand.
Key takeaways:
Let’s embrace this journey with open minds and hearts, ready to be part of a future that’s not just happening but is ours to shape. Join the conversation, share your insights, and let’s collectively envision and build the world of 2024.
Enjoyed This Story?
Vincent Koc is a highly accomplished, commercially-focused technologist and entrepreneur a wealth of experience focused in data-driven and digital disciplines. Currently, Vincent serves as a data leader in Australia as well as a lecturer for artificial intelligence in the US.
Subscribe for free to get notified when Vincent publishes a new story. Or follow him on LinkedIn and X (formerly Twitter).
Get an email whenever Vincent Koc publishes.
Unless otherwise noted, all images are by the author

Navigating the AI Landscape of 2024: Trends, Predictions, and Possibilities was originally published in Towards Data Science on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.

Introduction
Welcome to a journey through the possibilities that 2024 holds for AI and technology. Here, each prediction is a potential window into a future filled with innovation, change and more importantly opportunity similar to the industrial revolution of the 1950’s. The 50’s witnessed the rise of digital computing, reshaping industries and societal norms. Today, artificial intelligence plays a similar role, forging the next industrial revolution.
Much like the the post-war technological boom, we are navigating 2024 with industries transforming, new skills in demand, and significant ethical considerations being raised. The views expressed here are all my own, and based on my personal, commercial, and academic experiences combined.
Table Of Contents — All Predictions & Trends:
- Generative AI Leaps From Hype To Center Stage
- Expect To See The Next Generation Of Neural Networks
- Every Data Platform Launches Their Vector Data Feature
- Rush To Control The Hardware And Platform Supply Chain
- 2024 Is The Year Of The AI Wearables & XR
- AI Agents Will Start Communicating With Other AI Agents
- Generative AI Modalities Will Expand
- Consumers & Regulators Push For More Democratized AI
- The New Era of AI-Infused Marketing Strategies
- The “Garbage In, Garbage Out” Dilemma Intensifies
- Purpose Built Smaller Foundational Models Commonplace
- The Dawn Of AI Marketplaces For Agents
- AI Products Will Go Beyond SaaS Model
- BYO AI Movement Pushes Need For Secure Digital Identities
- Conclusion & Key Takeaways

1) Generative AI Leaps From Hype To Center Stage
Poised to redefine tech’s ecosystem, generative AI shifts from a hype-cycle balloon that’s “going to burst” to a core strategy and more of a sure thing, just as the airships are making a comeback.
For large enterprises it’s a paradigm shift in how they approach problem-solving and innovation, as they move from experimenting to adopting with generative AI. This technological course correction is akin to the transformative wave brought about by the early adoption of cloud technologies, suggesting a similar, if not greater, impact on the tech ecosystem.
97% of Business owners already believe that generative AI tools such as ChatGPT will have a positive impact to their business (Forbes).
The landscape of 2024, therefore, promises to be one where generative AI is not just a buzzword but a critical driver of technological advancement and business transformation. Where AI strategy is strategy.

2) The Next Generation Of Neural Networks Starts Emerging
With doubts forming on the general cognitive abilities of transformer architectures powering LLMs and the race for AGI has fuelled the research community searching for the next best thing. We have seen some recent advancements as well as developments in existing technologies:
- SSM’s such as Mamba; a model that excels in linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. An alternative to transformer architecture that runs large language models today. It represents a leap forward in how AI processes and understands sequences, a fundamental aspect of human cognition.
- Neuro-symbolic AI blending the best of neural network’s learning capabilities with the precision of symbolic AI. This hybrid approach promises a more nuanced and sophisticated understanding of complex problems, bridging the gap between human-like reasoning and machine efficiency.
- and lastly AI alignment with self correcting models. The aim is to create models that can adapt and correct themselves without constant human intervention, moving closer to a form of generative independently and responsibly without large scale hallucination risks.
These new model architectures are painting a future where AI’s capabilities could rival human cognition and the limitations of generative AI today. Research is early however expect to see someone take a leap of faith and break ground in this space.

3) Every Data Platform Launches Their Vector Data Solution
With the reliance on vector databases for generative AI, we will see all the key data platform players to bring to market their flavour for solving this solution. Although vector databases are not a new concept, they are not traditionally part of the “modern data stack” and have been in the past used for search engines and other types of machine learning.
Vector databases are a key requirement for more complex use cases of generative AI such as conversational memory, searching your documents (RAG), and also multi-modal solutions such as indexing images. It’s no surprise in mid-2023 we saw an explosion in demand following multi-modal models becoming more accessible.

Demand for Vector Databases following OpenAI GPT-4 release in March 2023 — Google Trends (Worldwide)
With Databricks recently releasing their vector data solution we are likely to expect key modern data platform players such as Snowflake to follow this trend in 2024. Possibly other adjacent technology providers are also going to jump on the trend by providing various features and services. Nearly all database technologies will start calling themselves “vector stores” in 2024.
Alongside this adoption shift, we are likely to see skills expectation with senior data and software engineers to get more comfortable with concepts around vector indexes, semantic search solutions, embeddings and possibly even algorithms such as BM25.
To stretch we might see the acquisition or further funding rounds for some of the initial modern vector search solutions adopted by the Generative AI community such as Chroma, Weaveate, Pinecone, and Qdrant.

Github “stars” for open source vector database repositories. Growth aligns with GPT3.5 release — Source: Star-History & Github
In the open-source world of vector stores Milvus is currently the crowd favourite and established itself as the enterprise choice with its managed services, but recently Qdrant has made some exceptional headway with near exponential growth in 2023.
If you have some spare time read the four part detailed vector database breakdown given by fellow AI engineer Prashanth Rao for a great in-depth understanding of the capabilities and various providers of vector database solutions.

4) Rush To Control The Hardware And Platform Supply Chain
With the dominance of artificial intelligence there is an increasing importance to better control the supply chain end-to-end to hold the keys to innovation.
NVIDIA, for instance, a leader in chip manufacturing which has been a clear winner in the AI race. The question on everyone’s mind is whether NVIDIA will expand its horizons into the cloud computing realm, leveraging its hardware expertise to offer integrated AI cloud services. NVIDIA already has a cloud streaming service called Geforce Now offering high end graphics processing on-demand. Such a move could redefine the competitive landscape, offering NVIDIA a more direct influence over AI’s developmental trajectory.

Nvidia Share Price, Last 5 Years (NASD:NVDA) — Source: Nvidia Investor Relations
On the other side of the spectrum are cloud AI providers like Amazon and emerging AI players like Anthropic and Mistral. Their current reliance on external hardware sources for AI operations raises a crucial question: Will they follow in the footsteps of OpenAI, which has begun sourcing its own chips and Google with TPU’s and Coral AI? This strategy could signify a shift towards self-reliance and customization in AI hardware, potentially leading to more tailored and efficient AI solutions for the top AI providers.

Google Coral — Local AI Development Boards and Hardware — Credit: Coral AI
As everyone in the underlying hardware layer of AI will be rushing to further control their supply chain. Will chip manufacturer NVIDIA move to cloud? Will cloud AI providers such as Amazon or the likes of Antrophic follow OpenAI in sourcing their own chips? Will mobile chip makers like Qualcomm be the winners as they power the new AI mobile devices and wearables?
The trend towards vertical integration of AI underscores a larger narrative: control over AI hardware is becoming synonymous with control over the future of tech. We will expect to see new players muscle into the purpose built AI chips to serve cloud players, countries rushing to fuel microprocessor development and finally OpenAI getting into the chip game in early 2024.

5) 2024 Is The Year Of The AI Wearables & XR
This year, we’re witnessing an intimate revolution in how we interact with technology, with the world of AI and wearables fusing alongside extended reality (XR) devices. These devices are not just gadgets; they’re extensions of our digital selves, blending seamlessly into our daily lives.

Humane AI Pin — Source: Humane
Humane AI’s Pin (powered by Qualcomm Snapdragon processors) and Tab are redefining the wearable landscape. These devices offer a glimpse into a future where wearables are no longer just about tracking health metrics or receiving notifications. They are about enhancing human interactions, offering real-time AI assistance, and providing an augmented experience of the world around us.

Rewind AI Pendant — Source: Rewind
Rewind, another breakthrough product, is revolutionizing how we capture and relive our memories. Imagine a device that not only records moments as we experience them but also allows us to revisit, understand, reflect on our memories.
But it’s not just the new players making waves. Tech giants like Apple and OpenAI are stepping into the wearable arena, promising to bring their colossal innovation capabilities. Apple, with its track record in creating trendsetting devices, is highly likely to introduce wearables that integrate seamlessly with its ecosystem within or alongside their XR Apple Vision Pro, offering unparalleled user experiences.
OpenAI, on the other hand, could leverage its expertise in AI to introduce wearables that bring advanced AI functionalities right to our fingertips (or wrists). The potential for AI wearables that interact with generative AI models like ChatGPT is particularly exciting, offering a blend of convenience and intelligence unlike anything we’ve seen before.
Meta is another key player to watch. Their foray into VR wearables has already shown us the potential for immersive digital experiences. As they continue to innovate in this space, we can expect wearables that not only augment reality but create entirely new realms for us to explore and interact with.
In 2024, AI wearables are set to move beyond mere technology. They are becoming personal companions, digital assistants, and gateways to new realities. They represent a shift towards a more intimate and interactive relationship with technology, one where our digital and physical worlds intertwine seamlessly. This year, we’re not just wearing technology; we’re living it.

6) AI Agents Will Start Communicating With Other AI Agents
Envision an ecosystem where specialized agents, each with its unique expertise and knowledge base, interact and collaborate. With the development of AI “agents” we will continue to see the growth in this space heading into 2024.

AI Agents Market Map Dec 23 — Credit: Olivia Moore
We will see the advent of agents going beyond supporting individual needs like writing my email, solving a customer support issue or ordering my groceries to an ecosystem where agents will start to interact with other agents. This paradigm shift revolves closely with the concept of data products, where enterprises will have the opportunity to monetize their agents in the same way they did with their models and datasets. This will foster a new ecosystem of interconnected, intelligent agents.
We are seeing robotics and humanoids from companies such as Boston Dynamics and Tesla having to look at solving this problem as various robots need to co-exist and locally communicate the decide how to carry out a task.
Companies with strongholds of data within given verticals like Bloomberg (finance) and LexusNexus (law) are poised to be potential frontrunners in this domain. Bloomberg, with its stronghold in finance data, could introduce sophisticated finance agents and have already started on their own LLMs, while LexusNexus could leverage its vast legal information repository to develop legal agents. These agents, powered by their respective deep moats of data, would not only serve their direct users but also act as invaluable resources for other enterprises and systems to power a new digital workforce.
Expect to start seeing new agent solutions beyond digital workforce to agent orchestration, management, monitoring as well as players in the digital robotic process automation space such as UiPath as well as humanoid advancements for manufacturing and plant work start to play into this space with their existing experience of automating and robotics systems at scale.

7) Generative AI Modalities Will Expand
Going beyond the text, code, image, video and audio to new more immersive modalities and senses such as 3D, genomics, smell, taste and will start to come into the market in early forms.

Generative spatial AI to generate new town layouts — https://www.generativespatialai.com/
Generative AI is set to grow out of its current boundaries of text, code, image, video, and audio. We will embrace more immersive modalities that help science with protein structures and materials or engage additional senses like 3D, smell, and taste. These novel modalities are expected to emerge in their early forms, signaling the next wave of Generative AI use cases.
The rise of autonomous AI agents and multi-modal models, coupled with advancements in wearables and extended reality (XR), is paving the way for a more immersive and interactive experiences for consumers.
Imagine your dreams turned into a VR world, every game having a unique world tailored to your perspective?
With recent 3D modelling technologies (Gaussian splatting) were videos can be converted into 3d virtual realities we will see this grow to new heights with generative technologies.

A-Lab Berkeley, Robot Testing New Materials — Credit: Marilyn Sargent/Berkeley Lab
The biggest impact will come from material sciences and genomics. GNoME model developed by Google Deepmind has been used already to make breakthroughs in material sciences, discovering new crystal structures driving better batteries to more efficient computers.
These fields such as sciences are where the most profound research advancements are likely to occur.

8) Consumers & Regulators Push For More Democratized AI
The will be a continued push towards greater accessibility and inclusivity with AI, but challenges remain due to the complexities and costs of developing foundational AI models. This dichotomy sets the stage for increasing public demands for transparency and ethical oversight in AI.

EU AI Act — Proposed Levels of Risk — Source: EY
Concerns over privacy and the societal impact of AI are driving consumers and regulatory bodies, especially in regions like the EU where GDPR was the catalyst to modern data privacy laws, to advocate for more stringent governance of AI. This year, we expect to see strides in establishing frameworks for auditing AI models, standardizing accuracy, and introducing “report cards” for AI systems but there is still a long way to go.

Do Foundation Model Providers Comply with the Draft EU AI Act? — Source: Stanford CRFN
The focus on risk management in AI will become more pronounced. Enterprises will navigate a landscape where AI is not only a tool for innovation but also under close regulatory scrutiny. Unified frameworks and standards will emerge, guiding businesses in responsible AI adoption and ensuring that AI’s integration into mainstream society is safe and aligned with public welfare.

9) The New Era of AI-Infused Marketing Strategies
The marketing domain, traditionally commanding a lion’s share of enterprise budgets, is now navigating through a transformative landscape. The catalyst? The rise of chat-based tools like ChatGPT. These innovations are potentially leading to a noticeable decline in traditional search volume, fundamentally altering how consumers engage with information.
Greg Sterling ?? on Twitter: "A report from BofA argues that Google's search market share is down ever so slightly and attributes that to ChatGPT. (I question that.) I think a more interesting metric to look at would be search frequency; are people conducting as many searches on Google as they used to? pic.twitter.com/S9iBXR4biP / Twitter"
A report from BofA argues that Google's search market share is down ever so slightly and attributes that to ChatGPT. (I question that.) I think a more interesting metric to look at would be search frequency; are people conducting as many searches on Google as they used to? pic.twitter.com/S9iBXR4biP
In this evolving scenario, marketers find themselves at a crossroads. The ability to influence or monitor brand mentions in these AI-driven dialogues is still in its nascent stages. Consequently, there’s a growing trend towards adapting marketing strategies for a generative AI world. This adaptation involves a strategic reliance on traditional media in the short term, leveraging its reach and impact to build and sustain brand presence.
Simultaneously, we are witnessing a significant shift in the technological landscape. The move from browser-based tools to on-device applications is gaining momentum. Leading this charge are innovations like Microsoft Co-Pilot, Google Bard on devices such as Android, and the anticipated launch of Apple’s own large language model (LLM) sometime in 2024. This transition indicates a paradigm shift from web-centric interactions to a more integrated, device-based AI experience.

New Microsoft Surface X expected late 2024 — Source: Microsoft
This shift extends beyond mere convenience; it represents a fundamental change in user interaction paradigms. As AI becomes more seamlessly integrated into devices, the distinction between online and offline interactions becomes increasingly blurred. Users are likely to interact with AI in more personal, context-aware environments, leading to a more organic and engaging user experience. For tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Apple, already entrenched in the marketing services world, this represents an opportunity to redefine their offerings.

ChatGPT not knowing who I am — Source: Vincent Koc and OpenAI ChatGPT
We can anticipate the emergence of new “answer analytics” platforms and operating models in marketing to support answer engine optimisation. These tools will likely focus on understanding and leveraging the nuances of AI-driven interactions but potentially better leverage the training data to understand how the results might be portrayed for a given brand or product.
Digital marketeers will start to think more deeply about how they are indexed in these training datasets same as they once did with search engines.

Screenshot of Top Domains Crawled by Commoncrawl, Dataset used to train most Large Language Models — https://commoncrawl.github.io/cc-crawl-statistics/plots/domains.html
Moreover, the potential launch of ad-sponsored results or media measurement tools by platforms like OpenAI could introduce a new dimension in digital advertising. This development would not only offer new avenues for brand promotion but also challenge existing digital marketing strategies, prompting a reevaluation of metrics and ROI assessment methodologies.
As LLM’s migrate into devices, moving away from traditional web interfaces, the marketing landscape is poised for significant changes. Marketers must adapt to these shifts, leveraging both traditional media and emerging AI technologies, to effectively engage with their audiences in this new digital era. This dual approach, combining the impact of traditional media with the precision of AI-driven analytics, could very well be the key to success in the rapidly evolving marketing landscape of 2024.

10) The “Garbage In, Garbage Out” Dilemma Intensifies
As organizations increasingly pivot towards leveraging generative AI models and developing their own fine-tuned solutions, the spotlight falls sharply on the quality of input data. The classic saying in data management circles of “garbage in, garbage out” is bubbled up again as data quality is now back on the table.

Trend for: Data Quality Topic — Source: Google Trends Worldwide
Organisations and leaders confront the harsh reality that high-quality, accurately labeled data is the cornerstone of effective AI deployment. The issue goes beyond the obvious availability of data; it’s about its relevance, accuracy, and the context it provides. Issues of bias and misguided training data can spell disaster for the output of a model.

Range of biases have been found in a range of training data used by Large Language Models. — Source: Bias and Fairness in Large Language Models: A Survey — arxiv
However, the challenges don’t stop there. Existing data and AI pipeline technologies, which once seemed adequate, are now being pushed to their limits. They are often found wanting in the face of the nuanced demands of advanced AI models. This gap between capability and requirement necessitates an evolution in data processing tools and methodologies.
The 2023 Data Integrity Trends and Insights Report uncovered poor data quality as a pervasive theme for organizations across the industry, with 70% of those with low levels of trust in their data pointing to data quality as the biggest challenge to making confident decisions.
Furthermore, the pursuit of AI excellence comes with its own set of logistical hurdles. The intensive compute power required for these sophisticated AI models translates to a substantial demand for GPUs.

Meme depicting the “GPU shortage”
But this isn’t just about having the financial muscle to invest in hardware; it’s about the availability of these resources in the market. As more players enter the AI arena, the scramble for GPUs intensifies, leading to potential bottlenecks in AI development and deployment which adds further complexity to the ability for organisations to adapt to the normal in AI.
As 2024 unfolds, we witness a renewed focus on data quality and infrastructure enhancement, shaping the trajectory of AI development.

11) Purpose Built Smaller Foundational Models Commonplace
2024 might very well be the year of the small foundational models. These specialized, purpose-built AI models are set to take center stage, outshining their generalized counterparts in efficiency and precision.
Organisations now have a number of options of using readily trained generalised large language models such as OpenAI GPT, Google Bard, Anthropic Claude [RL model in chart below] or venture into the world of building your own.

LLM development stages, pioneered by the InstructGPT paper, leading to ChatGPT. This figure is adapted from Chip Huyen’s post “RLHF: Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback” — Source: Argilla
With options to fine-tune which is taking the base/foundational language model but teaching it new things (as you would imagine fine tuning a car to go faster) or go deep into creating your own foundational (base) models altogether.

Open AI GPT Custom Model for Enterprise — Source: OpenAI
With generalised models such as the GPT models with 100 billion parameters (or “switches” in its model programming) would cost roughly upwards of $4million to rebuild. OpenAI has also recently started offering a service for enterprise to “build your own GPT” for pricing starting from $2–3million.
Organizations that have either developed their own foundational models or fine-tuned existing ones to their specific use-cases are poised for success. This approach aligns with the 80:20 rule, where the focus is on smaller, tailored models that cater to specific needs rather than attempting to appeal to the masses with generalized solutions.
The true value for organizations lies in the ability to develop these purpose-built models for discrete tasks. Not only do these models offer higher accuracy and relevance, but they also present new monetization opportunities. In a world increasingly driven by specialized needs, these models become invaluable assets, offering solutions that are both effective and economically viable.
Moreover, the trend is shifting away from relying solely on large, general-purpose models as they are not quite perfect for every need. Many organizations have built solutions on top of these broad models, acting as “thin wrappers” that offer limited scope for customization and scalability. While these solutions may have been a stepping stone, they are unlikely to provide the long-term value that developing proprietary models can offer.

Generalised Model Availability and Quality Prediction — Source: Sequioa Capital
The winners in this evolving landscape will be those who invest in developing their own models generalised or small foundational models to plug gaps in the generalised space. This strategy not only increases accuracy and effectiveness but also reduces cost overheads. Smaller models are not only cheaper to run but also quicker to adapt and easier to manage.
This leads to the concept of “Total Cost of Modelling,” where the benefits of developing and maintaining these models outweigh the initial investment, offering a more sustainable and cost-effective approach in the long run.
As we look towards 2024, it’s clear that the ability to create and leverage small foundational models will be a key differentiator in the competitive AI market. This shift marks a significant move towards more personalized, efficient, and economically sound AI solutions.

12) The Dawn Of AI Marketplaces For Agents
AI marketplaces are emerging as adaptive and responsive platforms, reshaping the way we think about technology transactions and interactions.

OpenAI GPT Store, Launching in 2024 — Source: OpenAI
Leading the charge, OpenAI is poised to unveil its much-anticipated “GPT marketplace” in early 2024, setting a new benchmark in the AI arena. This move is expected to open the floodgates, with other tech giants like Meta quickly following suit. We could witness an array of players, from established giants like Amazon, Apple and even Bytedance to emerging startups, diving into this space.
But the ripple effect of this revolution extends beyond traditional tech entities. With the growth of autonomous agents and the surge in wearable technology, there will be the Apple iPhone and App Store moment again. Developers will see this as the next gold rush of opportunity.
In this transformative phase, the AI marketplace phenomenon is expanding its reach from B2B to B2C sectors. We’re likely to see a diverse range of players trying their hand at this, each bringing unique value propositions to the table. From consumer-focused AI applications to enterprise-level solutions, the spectrum of offerings in these marketplaces will cater to a wide array of needs and aspirations.

13) AI Products Will Go Beyond SaaS Model
With the proliferation of AI marketplaces and tools, traditional pricing strategies are being re-evaluated, making way for innovative approaches that cater to the unique nature of AI services.

Usage Based Companies — Source: Open Venture Partners
We are likely to witness a significant shift from the conventional app store pricing model to more dynamic, consumption based billing systems. These models, reminiscent of utility billing like phone lines, are poised to become more prevalent, aligning with the concept of renting AI agents. In this setup, customers would pay based on the extent and nature of their AI usage, offering a flexible and potentially more equitable pricing structure.
But the evolution doesn’t stop there. The increasing adoption of AI marketplaces and tools is also paving the way for varied pricing strategies and novel business models. This change is driven by the need to accommodate a wide range of AI applications and services, each with its own value proposition and usage patterns. This could see the trial of both the revenue share (App Store) or the royalties on usage (Spotify) model for developers and their AI services or agents on marketplaces.
Another emerging model could be performance-based pricing, where charges are aligned with the outcomes or results delivered by the AI tool. Such a model would be particularly appealing in sectors where AI’s impact can be quantitatively measured, like in marketing analytics, financial forecasting, or even creative industries.

Bundled vs Unbundled Strategies in Pricing — Source: Matt Brown
Furthermore, as AI continues to penetrate various sectors, cross-industry partnerships could give rise to bundled services. These bundles could combine AI tools with traditional software services, offering a comprehensive package that addresses a wider array of business needs.
The onset of these new pricing models and strategies reflects a marketplace that is rapidly adapting to the unique challenges and opportunities presented by AI. As businesses and consumers alike become more familiar with AI capabilities, the demand for flexible, transparent, and value-aligned pricing models will likely intensify.

14) BYO AI Movement Pushes Need For Secure Digital Identities
Expanding modern and generative AI tools will lead the expansion of digital footprints necessitating secure, portable digital identities, where the challenge is to balance robust security with user accessibility. Users will expect a personalised experience where preferences, history and context will be key to using many AI services across the web.
Banks and e-government platforms are emerging as potential custodians of these single digital identities and personal preferences. This consolidation points towards a streamlined, more secure digital existence. But it’s not just about security; it’s about the seamless integration of our digital selves across various platforms.
“Bring Your Own AI” (BYO AI) ties directly into this. Imagine carrying your digital preferences, learning styles, and even shopping habits seamlessly from one digital interaction to another. This portability isn’t just convenient; it’s transformative. It allows for a level of personalization and efficiency previously unattainable. Wearable are also becoming integral to managing our digital identities. By constantly learning from our interactions, they evolve into personal data hubs that not only understand our preferences but anticipate our needs.
The integration of AI into work environments means that our digital preferences could automatically adjust settings in office applications, communication tools, and even physical workspaces. Imagine entering a meeting room where the lighting, temperature, and even digital displays are automatically tailored to your preferences.
However, this level of personalization and data integration raises questions about privacy and data usage. As these digital identities become more intricate and intertwined with AI, the potential for them to be leveraged for advertising digital experience providers for hyper-personalization is significant. This could lead to a new era of contextual advertising and consumer engagement, where promotions are not just targeted but deeply integrated into our digital personas.
This integration of identity with AI will redefine how we interact with technology, both in personal and professional spheres, leading to a more personalized, efficient, and connected existence. As we embrace this future, the importance of ethical considerations and privacy safeguards becomes more crucial than ever.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
As we look towards 2024, the potential of AI and technology to reshape our world is undeniable. Each of these predictions offers a glimpse into a future where innovation, responsibility, and inclusivity go hand in hand.
Key takeaways:
- Generative AI Emerges as a Core Technology Strategy: Marking a shift from hype to mainstream adoption across various sectors.
- Advancements in Neural Networks Edge Closer to AGI: New architectures like Mamba and neuro-symbolic AI enhance cognitive capabilities significantly.
- AI Wearables and Extended Reality (XR) Gain Prominence: Offering augmented human experiences and interactions in daily life.
- Interconnected AI Agents Create a New Ecosystem: Specialized AI agents communicating with each other revolutionize industry dynamics.
- Secure Digital Identities Become Crucial in the BYO AI Era: The rise of portable digital identities managed by banks and e-government platforms.
Let’s embrace this journey with open minds and hearts, ready to be part of a future that’s not just happening but is ours to shape. Join the conversation, share your insights, and let’s collectively envision and build the world of 2024.
Enjoyed This Story?
Vincent Koc is a highly accomplished, commercially-focused technologist and entrepreneur a wealth of experience focused in data-driven and digital disciplines. Currently, Vincent serves as a data leader in Australia as well as a lecturer for artificial intelligence in the US.
Subscribe for free to get notified when Vincent publishes a new story. Or follow him on LinkedIn and X (formerly Twitter).
Get an email whenever Vincent Koc publishes.
Unless otherwise noted, all images are by the author
Navigating the AI Landscape of 2024: Trends, Predictions, and Possibilities was originally published in Towards Data Science on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.